Helium
Helium: A strategic and highly sought-after resource
Due to its extreme rarity on earth and its unique physical and chemical properties, helium is a highly sought-after resource.
Why is helium a strategic resource?
A restricted number of production sites
Helium production sites are limited and concentrated in a minority of countries, particularly in the United States, Qatar, Algeria, Australia, Russia and Poland.
Uses booming
Helium is a key resource essential for many industries, such as new technologies. The number of uses keeps increasing every day!
Unequally distributed production
The places of consumption do not match with production areas. As a result, Western Europe imports all its helium needs at high energy costs.
No effective substitute
Helium has unique properties that most of users have so far not been able to substitute.
Unsustainable synthesis
Helium synthesis is possible but complex and inefficient to represent a viable alternative.
Dependency to natural gas
The majority of helium reserves, mostly discovered by chance, are a by-product of natural gas fields.
The worldwide helium market
Helium has become a strategic resource, where demand is growing and production is unequally distributed. In a context where the resource is becoming increasingly scarce, the cost of helium continues to rise (+195% over the last 5 years).
It is therefore more than essential to produce the resource locally, and in a short circuit, in order to participate in European sovereignty, while reducing environmental impacts.
Consommation
No Data Found
Production
No Data Found
Source: IHS Markit
Gaseous Helium average price (€/m³)
No Data Found
Source : 45-8 ENERGY data compilation – Gaseous helium in B402X cylinder
Helium physical properties
Helium: unique, rare and valuable
It does not react and does not alter the material with which it is in contact.
More than air and therefore the ideal gas for lifting airships and festive balloons.
This property makes it very effective for deep-sea diving.
This gives it the quality of excellent cooler, especially for medical MRIs, cryogenics or superconducting magnets.
It can be produced and used safely whatever is the context.
It is a neutral gas that can be used for many applications without any risk.
It is a tiny molecule that escapes through any crack, making it ideal for leak detection.
Inert
Helium does not react and does not alter the materials with which it is in contact.
Lightweight
Lighter than air, helium is the ideal gas for lifting airships and festive balloons.
Poorly soluble
The low solubility of helium makes it very effective for deep-sea diving.
Very low liquefaction temperature
Helium has the quality of an excellent cooler, especially for medical MRI, cryogenics or superconducting magnets.
Non-flammable
Helium can be produced and used safely in any context.
Non-toxic
Helium is a neutral gas that can be used for many applications without any risk.
Volatile
Helium is a very small molecule that escapes through any crack, making it ideal for leak detection.
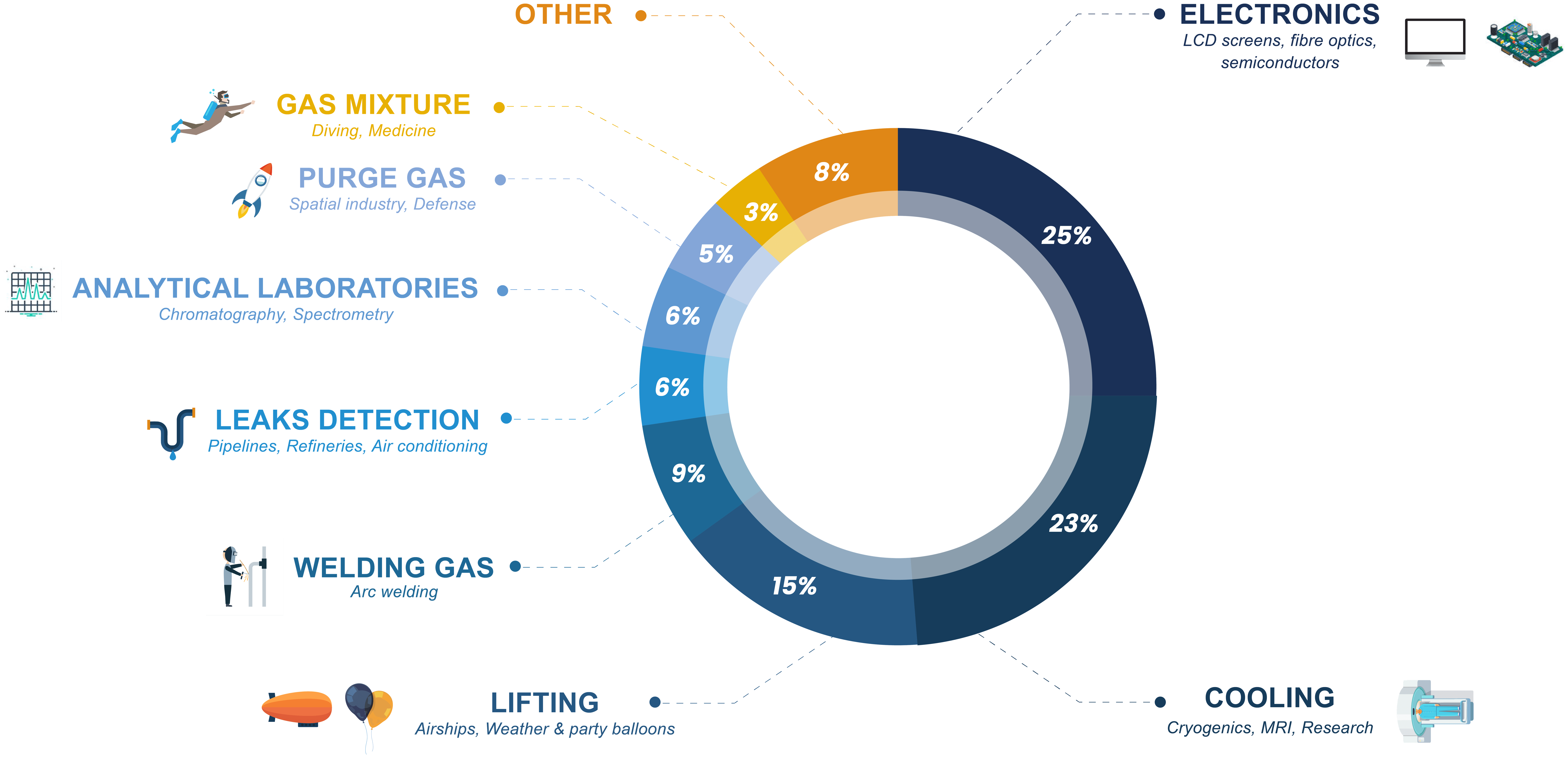
Helium uses
Helium is a necessary resource for many industries. Often unknown, the uses of helium are varied.